Capacitance Formulas
If you are looking for help on the Concept of Capacitance you have come the right way. After going through this page you can have an idea on Capacitance Formulas and can solve various questions related to them. Check out the Formulas on Capacitance such as Capacitance of Conductor, Capacitance of Spherical Conductor, Parallel Plate Capacitor, etc.
Make the most out of the Physics Formulas for several concepts and master the relevant topics easily. Just access the relevant Capacitance Cheat Sheet while solving concerned problems and apply them to get results easily.
Capacitance Formula Sheet
1. Capacitance of a conductor
Capacity of storing charge
C = \(\frac{Q}{V}\)
Unit → farad = \(\frac{\text { coulomb }}{\text { volt }}\)
2. Capacitance of a spherical conductor
C = 4πε0R
R → Radius of conductor.
3. Common potential when two charged conductors are connected
C = C1 + C2
Q = Q1 + Q2 = C1V1 + C2 V2
Common potential
V = \(\frac{\mathrm{C}_{1} \mathrm{V}_{1}+\mathrm{C}_{2} \mathrm{V}_{2}}{\mathrm{C}_{1}+\mathrm{C}_{2}}\)
Charge transferred
╬öQ = \(\frac{C_{1} C_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}\) (V1 – V2)
Energy loss
╬öU = \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{C_{1} C_{2}}{C_{1}+C_{2}}\) (V1 – V2)2
4. Capacitor (condenser)
An arrangement of conductors for increasing the capacitance. It has two conductors placed nearby, one is charged and the other is earthed.
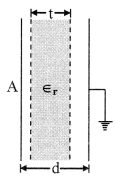
5. Parallel plate capacitor
C = \(\frac{\epsilon_{0} A}{d}\), Cm = ╬╡r = \(\left(\frac{\epsilon_{0} A}{d}\right)\) = ╬╡rC
If a dielectric of thickness t is placed in between, then
C = \(\frac{\epsilon_{0} A}{\left(d-t+\frac{t}{\epsilon_{r}}\right)}\)
(a)
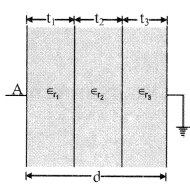
If slabs of thickness t1, t2, t3 …. tn of dielectric constantΓÇÖs ╬╡r1, ╬╡r2, …… ╬╡rn are placed in between
C = \(\frac{\epsilon_{0} A}{\left(\frac{t_{1}}{\epsilon_{r_{1}}}+\frac{t_{2}}{\epsilon_{r_{2}}}+\ldots .+\frac{t_{n}}{\epsilon_{r_{n}}}\right)}\)
and d = t1 + t2 + t3 + …. + tn
(b)
6. Spherical capacitor
When outer spherical shell is earthed
C = 4πε0εr \(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{1} \mathrm{R}_{2}}{\mathrm{R}_{2}-\mathrm{R}_{1}}\) ; R2 > R1
When inner sphere is earthed
C = 4πε0εr \(\frac{\mathrm{R}_{1} \mathrm{R}_{2}}{\mathrm{R}_{2}-\mathrm{R}_{1}}\) + 4πε0R2
7. Cylinderical condenser
C = \(\frac{2 \pi \epsilon_{0} \epsilon_{\mathrm{r}} \ell}{\log _{\mathrm{c}}\left(\mathrm{R}_{2} / \mathrm{R}_{1}\right)}\)
8. Capacitance of a two wire line
C = \(\frac{\pi \epsilon_{0} \epsilon_{1} \ell}{\log _{e}(d / r)}\) (d >> r)
l → length of each wire
d → distance between wires
r → radius of each wires
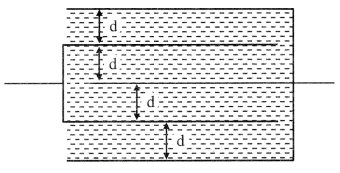
9. Multiplate capacitor
C = (n – 1) \(\frac{\epsilon_{0} \in_{r} A}{d}\)
A → area of each plate.
10. Energy stored in a capacitor
U = \(\frac{1}{2}\) CV2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\) QV = \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{Q^{2}}{C}\)
This energy resides in electric field. Energy density of electric field
U = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ╬╡E2 = \(\frac{\text { Total Energy }}{\text { Volume }}\)
11. Combination of capacitor
Series combination
\(\frac{1}{C}=\frac{1}{C_{1}}+\frac{1}{C_{2}}+\ldots \ldots+\frac{1}{C_{n}}\)
Q1 = Q2 = …….. = Q
V = V1 + V2 + V3+ ……… + Vn
Parallel combination
C = C1 + C2 + …….. Cn
V1 = V2 = …….. = V
Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 + …….. + Qn
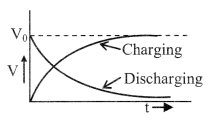
12. Charging and discharging of a capacitor through a resistance
Charging
q = q0 (1 – e-t/RC)
V = V0 (1 – e-t/RC)
I = I0 e-t/RC, I0 = \(\frac{V_{0}}{R}\)
V → P.d. across capacitor
q → charge on the capacitor
I → current through the capacitor
Discharging
q = q0 e-t/RC
V = V0 e-t/RC
I = – I0 e-t/RC
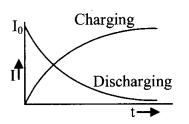
Time constant
while charging
τ = RC, time in which q = 0.63Q, V = 0.63V0 and I = 0.37I0
while discharging q = 0.37Q, V = 0.37V0 and I = 0.37I0
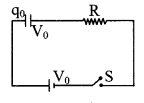
- In charging energy supplied by the battery up to steady state is V0q0
- Energy stored in capacitor as a electric field is \(\frac{1}{2}\)V0q0
- Energy loss during charges = \(\frac{1}{2}\) V0q0
13. Force of attraction between the plates of a capacitor
F = \(\frac{1}{2}\) ╬╡E2 A = \(\frac{Q^{2}}{2 \in A}=\frac{1}{2} \frac{C V^{2}}{d}\)
F = \(\frac{\sigma^{2}}{2 \epsilon}\)A
Seek help regarding concepts that you never seemed to understand in an efficient manner from Physicscalc.Com and clarify all your concerns.