Radio Activity Formulas
Do you feel solving problems on Radio Activity is difficult? Not anymore as we have presented the Radio Activity Formulas Complete List here. Use them during your homework or assignments and arrive at the solutions instantly. By availing the Radio Activity Cheat Sheet you can solve any problem be it complex or basic.  Have a glance at the Physics Formulas provided to know more info. Formula Sheet of Radio Activity includes topics like radioactive decay law, Half-life, Mean Life, etc.
Formula Sheet for Radio Activity
1. Radioactivity
The phenomenon of spontaneous disintegration of atoms is called radioactivity. Radioactivity is a nuclear property. Three types of rays, ╬▒, ╬▓ and ╬│-rays, are emitted from radioactive materials. These are called Becquerel rays, ╬▒-particles are doubly ionized helium atoms, ╬▓-particles are either electrons or positrons which are emitted with very high velocity (nearly velocity of light) and ╬│-rays are electromagnetic radiations of high frequencies with a very high penetrating power.
2. Units of activity
- 1 curie (Ci) = 3.7 × 1010 disintegration/s
- 1 rutherford (Ru) = 106 disintegration/s
- 1 becquerel (Bq)= 1 disintegration/s
3. Rutherford-suddy law or radioactive decay law
According to this law the rate of disintegration of active atoms at any time is directly proportional to the total number of active atoms present at that time.
(-) \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{dt}}\right)\) ∝ N
or \(\frac{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{dt}}\) = -╬╗N
or
![]()
– \(\frac{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{dt}}\) ΓåÆ rate of disintegration.
N → Total no. of active atoms present at that time.
4. Half-life
The time in which half of the active atoms disintegrate is called half life of that radioactive element.
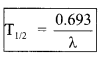
After a time equal to n half live \(\frac{1}{(2)^{n}}\) part of the element will remain undecayed.
\(\frac{N}{N_{0}}=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{t / T_{1: 2}}=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{n}\)
n = no.of half lives
5. Mean life (τ)
The mean life of a radioactive element is equal to the ratio of the sum of life-time of all the active atoms to the total number of active atoms.
τ = \(\frac{1}{\lambda}\) = 1.44 T1/2
![]()
6. Activity
The rate of disintegration of active atoms of an element \(\left(-\frac{\mathrm{d} \mathrm{N}}{\mathrm{dt}}\right)\) is called its activity (A).
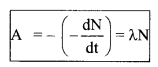
7. Emission of ╬▒-particles and energy spectrum
- By the emission of ╬▒-particles the atomic number of the parent nucleus decreases by two and the mass number decreases by four.
- The energy spectrum of ╬▒-particles is discrete.
- The emission of a-particles from the nucleus is explained by the tunnel effect.
![]()
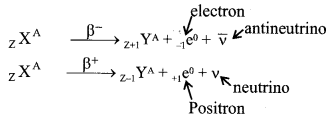
8. Emission of ╬▓-particles and energy spectrum
- By the emission of ╬▓–-particle the mass number remains unchanged but the atomic number increases by one and by the emission of ╬▓+ particle the mass number remains unchanged but the atomic number decreases by one.
- ╬▓-particles are formed and emitted due to transformation of neutrons and protons.
- The energy spectrum of ╬▓-particles is continuous.
In ╬▓-decay
9. Emission of ╬│-rays and energy spectrum
(i) When ╬▒ or ╬▓ – particle are emitted from the nucleus, the nucleus goes to an excited state. When it returns to its ground state, ╬│-rays are emitted.
(ii) The energy spectrum of ╬│-rays is discrete. By the emission of ╬│-rays no change occurs in the mass number and atomic number of the element.
In ╬│-decay
![]()
10. Carbon dating
It is a method of determining the age of archeological objects by C14 isotope; of carbon. The half lift of C14 is 5700 years.
Explore more Physics concepts formulas along with the Radio Activity Formula Sheet by visiting our reliable website ie., Physicscalc.Com