Thermodynamics Formulas
Not everyone feels the concept of Thermodynamics easy? To help such people we have curated the Thermodynamics Formulas that make your job simple. By going through the Formulae List of Thermodynamics you can answer any question framed on the topic quickly. The thermodynamics Formula Sheet listed over here covers the topics like Internal Energy, First Law of Thermodynamics, Isometric Charge, Isothermal Charge, and many more. People of any knowledge can refer to our Physics Formulas and learn the concepts effortlessly.
Formula Sheet for Thermodynamics
1. Internal energy
The total energy of constituent molecules. It is equal to the sum of internal kinetic energy and potential energy. Change in internal energy
dU = (U2 – U1) = nCvdT
Internal energy is a function of state only and its change does not depend on path.
2. First law of thermodynamics
The heat given is equal to sum of change in internal energy and work done by the system.
╬┤Q = dU + ╬┤W
3. Isometric or isochoric change
Volume remains constant i.e.,
dV =0
╬┤W = PdV = 0,
╬┤Q = dU = nCvdT.
4. Isobaric change
Pressure remains constant i.e.,
dP =0
╬┤Q = dU + ╬┤W = nCvdT + PdV
5. Isothermal change
Temperature remains constant i.e.,
dT =0
dU = nCvdT = 0, ╬┤Q = ╬┤W = PdV
6. Adiabatic change
No exchange of heat takes place i.e.,
╬┤Q = 0
∴ 0 = dU + δW
or
╬┤W = – dU.
7. Free expansion
Expansion in vacuum. No transfer of heat and no work i.e.,
δQ = 0, δW = 0 ∴ dU = 0.
8. Equation of state of gases
\(\frac{P V}{T}\) = Constant
PV = RT (for onle mole gas)
PV = nRT (for n-mole gas).
Isometric change:
V = constant, \(\frac{P}{T}\) = constant.
Isobaric change:
P = constant, \(\frac{V}{T}\) = constant.
Adiabatic change:
Entropy S = constant and ΔQ = 0
PV╬│ = constant
TV╬│-1 = constant
P1-╬│T╬│ = constant
Pd1-╬│ = constant.
The slope of P-V curve –
Isothermal process
\(\frac{\mathrm{dP}}{\mathrm{dV}}=-\frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{V}}\)
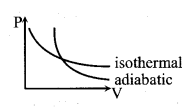
Adiabatic process
\(\frac{\mathrm{dP}}{\mathrm{dV}}=-\gamma \frac{\mathrm{P}}{\mathrm{V}}\)
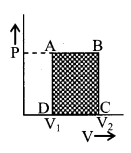
9. Work done by gases
W = \(\int_{V_{1}}^{V_{2}}\)PdV
Isometric change:
W = 0
Isobaric change:
W = P(V2 – V1)
Isothermal change
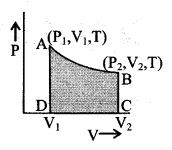
Wiso = nRTloge(V2/V1)
= nRT 2.303 loge(V2/V1)
= nRT loge(P1/P2)
Adiabatic change
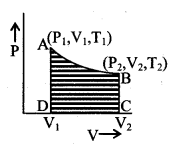
Wad = \(\frac{P_{1} V_{1}-P_{2} V_{2}}{\gamma-1}\)
= \(\frac{n R}{(\gamma-1)}\)(T1 – T2)
10. Elasticities of gases
Isothermal elasticity Eiso = P
Adiabatic elasticity Eadia = ╬│P
Take your subject knowledge to the next level by referring to the formulas of Physics provided by experts at Physicscalc.Com